Security issues might cause significant and long term financial and reputational damage. No company should take this risk lightly. It only takes one flaw or slip to derail everything a company has worked so hard to build up from the ground. And that’s why threat detection and prevention are so crucial.
Enterprises can gain a major advantage by being aware of these threats. Also understanding these security threats and how cybercriminals operate, companies can better protect themselves.
In this article, we will discuss the security threats and risks that your firm should be aware of to ensure strong cybersecurity defence.
Tap the play button to listen this article
WHAT IS THREAT DETECTION AND PREVENTION?
The ability of a company to monitor activity of its IT environment and identify true security risks is known as threat detection. On the other hand, threat prevention involves taking measures to prevent specific threats from entering the environment and causing harm. In order to effectively prevent dangers, you must first detect them in real time.
Security organisations use advanced threat detection software to detect and prevent threats. For example, the security information and event management (SIEM) system was the key system used in the former security operations centre (SOC) to gather threat detection data and identify threats. eXtended Detection and Reaction (XDR) is becoming more popular among businesses as it may improve the detection of unknown risks, automate research, and enable fast response to attacks.
There are several sophisticated threat detection software that uses artificial intelligence to identify threats, even if they don’t match a recognised malware or attack signatures. Examples: Next-Generation Antivirus (NGAV), solutions based on user behaviour analytics, and tools specifically designed for detecting and mitigating ransomware attacks.
WHAT ARE THE VARIOUS THREATS TO AN ORGANISATION?
Organisations face a multitude of threats that can disrupt their operations and jeopardise their success. Let’s have a look at some of them:
APTs (Advanced Persistent Threats)
When cybercriminals engage in Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs), they prefer to take their time. They secretly penetrate a computer network and meticulously identify entry and exit points that will allow them to remain undetected.
Once inside a company, they investigate, install harmful viruses, and steal important data and sensitive information.
To breach a company’s cybersecurity, they employ advanced technologies like malware and computer hacking techniques. These cybercriminals are persistent and prefer sneaky methods to gain access to a company and create chaos.
An APT typically progresses through 05 stages to maximise its impact:
Infiltration of Access:
APTs employ various tactics to gain unauthorised access to systems, such as phishing, trojan horses, and malware. They may also take advantage of human vulnerability, so it’s important to train employees on how to stay safe online.
To avoid access infiltration, you can use insider threat detection tools like EmpMonitor. This tool not only identifies any insider threats but also empowers you to tackle them effectively.
Grip Strengthening:
The ability of an Advanced Persistent Threat to gain a foothold within a firm is its strength. They must devise a method for entering and exiting the system without being detected. These guys use digital backdoors and tunnels to help them do it.
Invasion of the system:
Once APT attackers gain a lot of control over a system, they won’t stop. They will keep finding ways to break passwords and get administrator access. Once they have that kind of power, they can easily get the data they want without much resistance.
Lateral Activity:
Cybercriminals are currently playing in the business world. They’re exploring different parts of computer systems to find more sensitive databases and servers nearby. They use malware to steal data and then sneak it out of the network using backdoors. That’s how a breach starts.
To stop this, the best thing you can do is to use a special software for threat detection and protect the system better.
Deep Manipulation:
The APT attackers have complete control over the company at this phase, erasing all signs of their cyber footprint and constructing a reliable backdoor for future use. This extends the life of the cyber attack within the system.
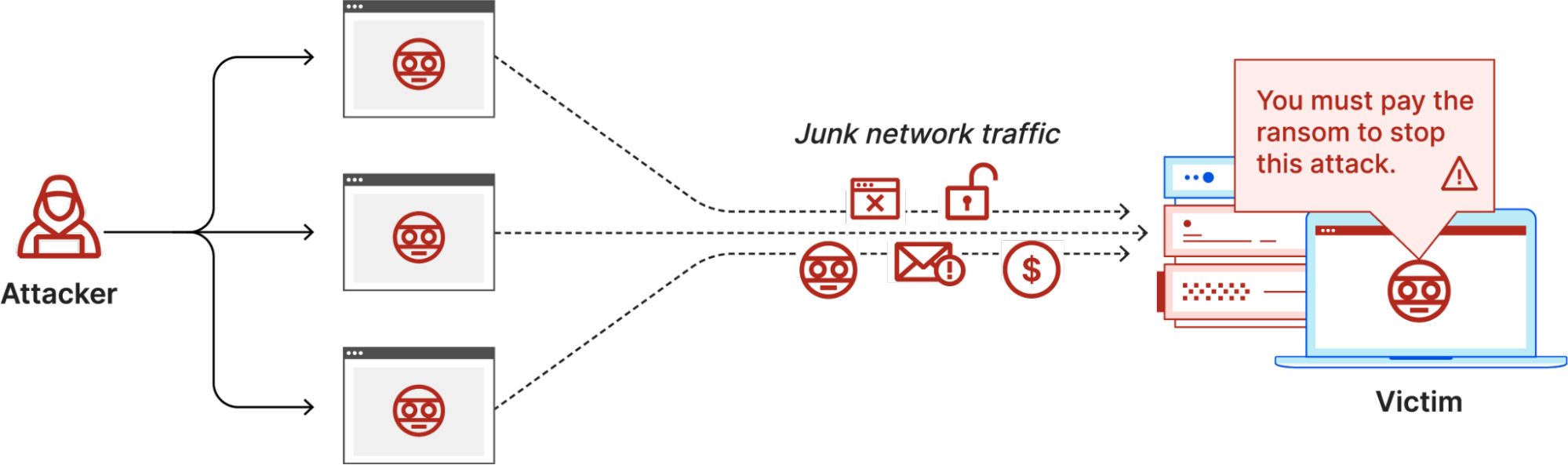
DDOD (Distributed Denial of Services)
When hackers use Distributed Denial of Service (DDOS), their main goal is to make a website stop working.
Basically, they overwhelm the website’s network with fake requests, which causes the system to become overloaded and crash. This means, regular users won’t be able to access the website. It can lead to significant losses in productivity because of these disruptive interruptions.
Resisting a Distributed Denial-of-Service attack is difficult because the attack comes from many different sources. Think of it like a rowdy crowd gathering in front of a restaurant’s entrance, making it impossible for confirmed guests to enter and disrupting the restaurant’s normal operations. Similarly, credit card and digital wallet payment gateways are often targeted by DDoS attacks.
The first DDoS attack happened on September 6, 1998, when Internet Service Provider Panix became unreachable to its clients due to a flood attack. Another notable occurrence occurred in 1997 when Khan C. Smith demonstrated a DDoS attack that disabled online access to the Las Vegas strip for about an hour.
Ransomware
Ransomware is a type of virus used by hackers to extort money from companies. They break into the company’s network and encrypt important data or sensitive customer information. Then, they threaten to expose the data unless the company pays a ransom.
Ransomware has proven to be a powerful cybercrime method for blackmailing businesses. Examples include attacks on companies in Atlanta, Georgia, and Baltimore, Maryland.
The attackers use the information they find in the compromised network to trick employees. They might send innocent-looking attachments or links to lure them into opening them.
The first known ransomware attack was the AIDS Trojan created by Joseph Popp in 1989. This malware encrypted important data and demanded payment for its release. However, Popp was spared from the trial because he was mentally ill. Instead, he decided to donate the money he made from the malware to AIDS research.
Phishing
Phishing is exactly what it implies. It is a type of cyber attack where hackers try to trick you into giving them your personal information, like passwords and credit card numbers. They do this by sending emails that look real and urgent.
The word “phishing” comes from “fishing” because hackers are like fishermen casting a line, hoping you’ll take the bait. The term was first used in 1995 by Koceilah Rekouche, who used cracking tools called AOHell.
BotNet:
A botnet is a combination of “robot” and “network.” It is the aggregate name for private computers infected with malware, allowing hackers to access them remotely without the computer owners’ knowledge.
Botnets are used by fraudsters to carry out various malicious activities such as distributing spam, launching DDoS attacks, and stealing data. To effectively manage and manipulate targeted networks, botnets require precise coordination and understanding.
In order to avoid cyber threat detection, the architecture of botnets has significantly improved. They employ applications that disguise themselves as genuine clients connecting to existing servers. Cybercriminals can then control these botnets remotely through peer-to-peer networks.
Cryptojacking:
Cryptocurrency is all the rage these days, and it relies on the mining approach to generate additional revenue. Cybercriminals have begun to infect and hijack other slave workstations, to engage in bitcoin mining through deceptive techniques such as phishing.
The victims of these cyber attacks are often unaware of the fact that their computing resources are being used to generate bitcoins. This unauthorised usage, commonly referred as cryptojacking, can significantly slow down the affected PCs.
Security Threats’ Typical Victims:
Cybercriminals use deceptive methods to harm organisations for various motives, including espionage, financial gain, and commercial destruction. They often target valuable organisations because High-value targets generally yield big financial incentives. Here are some examples of significant targets:
- Countries can face instability and chaos if sensitive information from their government gets exposed.
- Multinational corporations possess advanced technology or valuable ideas that make them attractive targets.
- Government agencies and critical infrastructure are also frequently targeted.
- Identity thieves often go after databases that contain personal information (PII) of individuals.
HOW CAN YOU PROTECT YOUR COMPANY FROM THREATS?
Protecting your company from threats requires a proactive approach that encompasses various measures:
Continuous Monitoring
Immediate and emerging threats necessitate constant vigilance, not just once-in-a-while, but every few months. Attackers can strike at any time, so it is necessary to keep constant surveillance of your potential attack surface.
As your application environment grows and evolves, continuous monitoring becomes even more important. Keeping track of risks becomes increasingly challenging with the release of more apps. You may continuously expose and discover dangerous areas that unscrupulous parties try to exploit using continuous monitoring.
Employee monitoring software, like EmpMonitor, is a useful tool for tracking and monitoring your employees’ actions. It is one of the top insider threat detection tools available. Be it a physical workplace or remote. It can help in threat detection by providing insights into employee activities, including their online behaviour, application usage, time spent on different tasks, and more.
Analytics on cybersecurity:
After implementing continuous monitoring, work to improve your cybersecurity posture over time. One way to achieve this is by using analytics to assess your company’s performance relative to competitors, supply chain issues, user behaviours, and other relevant factors. Based on the analysis, improvements can be made, resulting in higher-excellent ratings. A higher score indicates a safer workplace.
Make Security Training Available
Even with advanced and costly data security measures in place, a single click on a malicious link or the installation of fake software can compromise your entire system. To mitigate such risks, businesses must provide comprehensive training on common cyber threat detection and how to respond. Additionally, your employees should be aware of your cyber security policies and how to report any suspicious activity.
Now is the ideal time to secure your future with insider threat detection tools. Similar to getting life insurance at a younger age, obtaining threat detection software early can prevent potential issues and financial burdens down the line.
Establish strict password policies:
To protect your password-protected data from attackers, it’s important to manage your passwords effectively. Please set a password policy that requires employees to change their passwords regularly, avoid using the same password for several accounts, and use unusual characters.
Get Vulnerability Evaluations:
A vulnerability assessment is the best way to assess your company’s data exposures. Vulnerability assessments can help you find access points into your system by simulating attacks and testing them. After these tests, security experts analyse the results and provide recommendations for strengthening network and data security measures.
Prioritisation of Risks
Not all threats are the same, and some vulnerabilities are more dangerous than others. This is especially important to consider when it comes to third-party supply chain risk. For example, a vendor with private data, such as company payroll data, poses a greater risk than one who does not have access to personally identifiable information.
Security ratings can assist you in prioritising your suppliers so that you can focus your resources on the ones who need them the most. In addition, cross-referencing a vendor’s security rating with other critical data points–for example, their closeness to sensitive data or the amount of work they provide for your organisation–can help you figure out which suppliers are the most concerning.
Read More
Cybersecurity for Remote Workers: Why it is Essential?
What is Data Security|07 Threats to Look-Out for in 2022
Final Words!
“Knowledge is power,” as we’ve all heard, but in the case of threat detection, knowledge is both power and defence. The more you know about your network, third-party providers, and other elements, the better your chances of defending yourself against cybersecurity assaults and vulnerabilities are.