In today’s digital-first world, businesses, healthcare providers, engineers, and even marketers rely on telemetry data to improve decision-making and optimize processes. From tracking spacecraft performance to monitoring employee productivity in hybrid workplaces, telemetry has become the silent powerhouse driving efficiency and growth.
This comprehensive guide will break down the telemetry data meaning, its applications, benefits, challenges, and why it’s critical for organizations in every industry. We’ll also explore how companies can maximize value by combining telemetry with tools like analytics and employee monitoring software.
In a hurry? Listen to the blog instead!
What Is Telemetry Data?
It refers to the collection, transmission, and interpretation of information from remote sources. Imagine sensors on a car engine reporting fuel efficiency, or an app tracking user activity in real time. This constant stream of raw information is telemetry in action.
Unlike traditional data, telemetry is designed for continuous monitoring. It provides a dynamic, near-real-time view of systems, making it invaluable for industries like IT, aviation, healthcare, and business operations.
In simple terms, telemetry data means: information automatically collected from a system, transmitted over networks, and analyzed for insights without manual intervention.
Why Does Telemetry Data Matter Today?
The rise of digital platforms and connected devices has created an unprecedented demand for telemetry data. Organizations now depend on this information to:
- Monitor systems for early signs of failure.
- Ensure compliance and security in sensitive environments.
- Enhance product design and customer experience.
- Track workforce performance across global teams.
- Streamline decision-making through predictive insights.
From self-driving cars to smart wearables, telemetry enables businesses to act quickly and accurately in fast-changing environments.
A Brief History Of Telemetry
The concept of telemetry is not new. It originated in the 19th century when scientists first used remote monitoring to collect environmental and weather data. Over time, this practice expanded into aerospace, military, and medical fields.
Today, the digital revolution has transformed telemetry data into a cornerstone of modern innovation. Cloud computing, IoT devices, and advanced software have made it easier to collect, store, and analyze telemetry at scale.
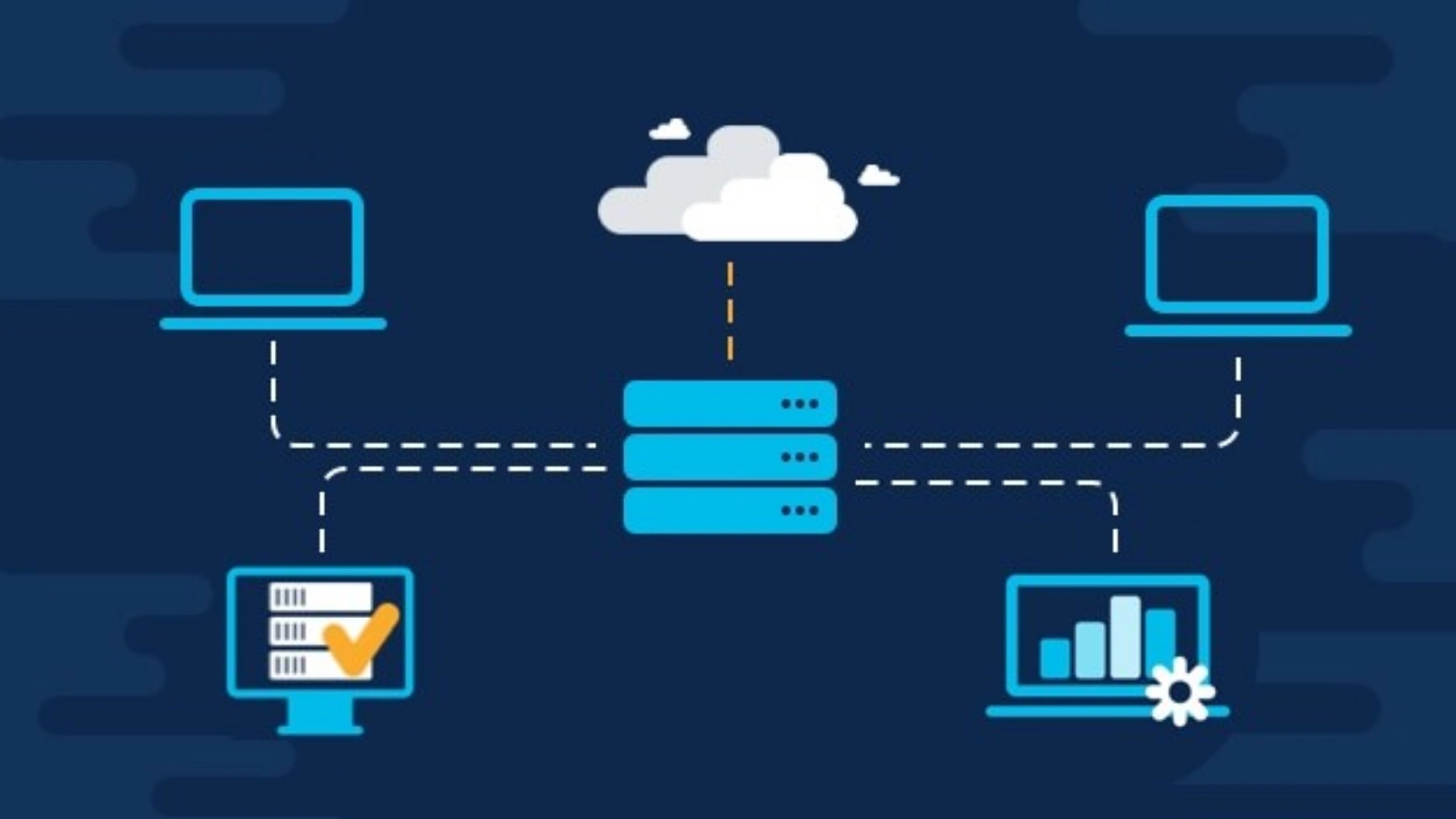
How Telemetry Data Works?
To understand the power of telemetry, let’s break down its process in detail:
1. Sensors Collect Data:
Specialized sensors or devices are embedded in equipment, vehicles, or systems to continuously capture metrics such as temperature, pressure, energy usage, machine speed, GPS location, or even user behavior. These sensors ensure accurate real-time monitoring without requiring manual intervention.
2. Transmission:
Once collected, the raw data is transmitted securely using communication networks like Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, satellite links, or cellular (4G/5G) connections. The choice of network depends on the use case, for example, satellites for remote mining sites or 5G for smart city applications. Data encryption ensures secure transmission during this step.
3. Storage & Processing:
The transmitted data flows into centralized platforms, often cloud-based, where it is organized, cleaned, and structured. Data preprocessing removes noise, duplicates, or errors, ensuring the information is reliable for analysis. In many cases, edge computing is also used to process some data locally before sending it to the cloud for faster decision-making.
4. Analysis & Insights:
Advanced analytics tools, machine learning models, and visualization dashboards interpret the processed data. This stage transforms raw metrics into meaningful insights, for instance, detecting patterns, predicting failures, or identifying inefficiencies. Businesses gain a clear picture of what is happening in real time and what may happen next.
5. Action:
The final step is where organizations put insights into practice. The analyzed data drives automated responses, triggers alerts, or supports informed decision-making. For example, predictive maintenance systems can schedule equipment repairs before breakdowns occur, while logistics companies can optimize delivery routes instantly based on live telemetry.
6. Continuous Feedback Loop:
This cycle operates non-stop, feeding back new information to sensors and systems. The continuous loop ensures businesses always have fresh, accurate, and actionable intelligence to stay efficient, reduce risks, and improve outcomes.
What Are Some Real-Life Examples Of Telemetry Data?
While the term might sound highly technical, telemetry quietly powers many aspects of our daily lives. Here are some common ways it shows up:
1. Fitness Trackers Monitoring Heart Rate and Steps:
Wearable devices like smartwatches collect real-time data on heart rate, step count, sleep cycles, and calories burned. This information helps users track fitness goals and detect potential health concerns early.
2. Cars Sending Diagnostics About Fuel Consumption and Tire Pressure:
Modern vehicles are equipped with sensors that measure fuel efficiency, tire pressure, and engine health. This telemetry data can trigger dashboard alerts, support predictive maintenance, and even send updates to service centers remotely.
3. Mobile Apps Analyzing User Interactions:
Apps use telemetry to track which features people use most, how long they stay on the app, and where they drop off. Developers then optimize app performance and user experience based on these insights.
4. Hospitals Tracking Patient Vitals in Real Time:
Telemetry in healthcare includes continuous monitoring of patient vitals like blood pressure, oxygen levels, and ECG data. Doctors can receive instant alerts about irregularities, allowing faster response during emergencies.
5. IT Systems Measuring Server Performance and Uptime:
Servers and IT infrastructure constantly generate telemetry data about CPU usage, bandwidth, and uptime. This ensures smooth digital operations, helps prevent outages, and supports cybersecurity monitoring.
These examples prove that telemetry data is everywhere, powering convenience, safety, and better decision-making.
What Are The Different Types Of Telemetry?
Telemetry can be classified based on how data is transmitted and applied. Businesses choose the right method depending on scale, speed, environment, and system requirements. The most common types include:
1. Wired Telemetry:
Data is transmitted through physical cables such as Ethernet or fiber optics. This method is highly reliable and less prone to interference, making it suitable for controlled environments like laboratories, research facilities, or industrial plants where stable connectivity is critical.
2. Wireless Telemetry:
Using technologies like radio signals, Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, or cellular networks, wireless telemetry provides flexibility and mobility. It is widely applied in areas such as agriculture (monitoring soil moisture), logistics (vehicle tracking), and healthcare (wearable devices), where wired setups are impractical.
3. Satellite Telemetry:
Ideal for remote or hard-to-reach areas, satellite telemetry enables long-distance monitoring of assets like ships, aircraft, and spacecraft. It ensures uninterrupted communication even where cellular or wired networks are unavailable, which is why it’s heavily used in defense, aviation, and maritime operations.
4. IoT Telemetry:
Powering the Internet of Things (IoT), this type uses connected sensors and smart devices to collect and transmit data across networks. From smart home appliances and industrial automation systems to patient monitoring in healthcare, IoT telemetry enables real-time decision-making on a massive scale.
These categories show how adaptable telemetry is, scaling from highly localized operations to global systems, making it a backbone for modern innovation.
Read More!
Post-Pandemic Chapter Of Employee Monitoring Software |
6 Free Monitoring ToolsBehavior Analytics- Top Applications 2022
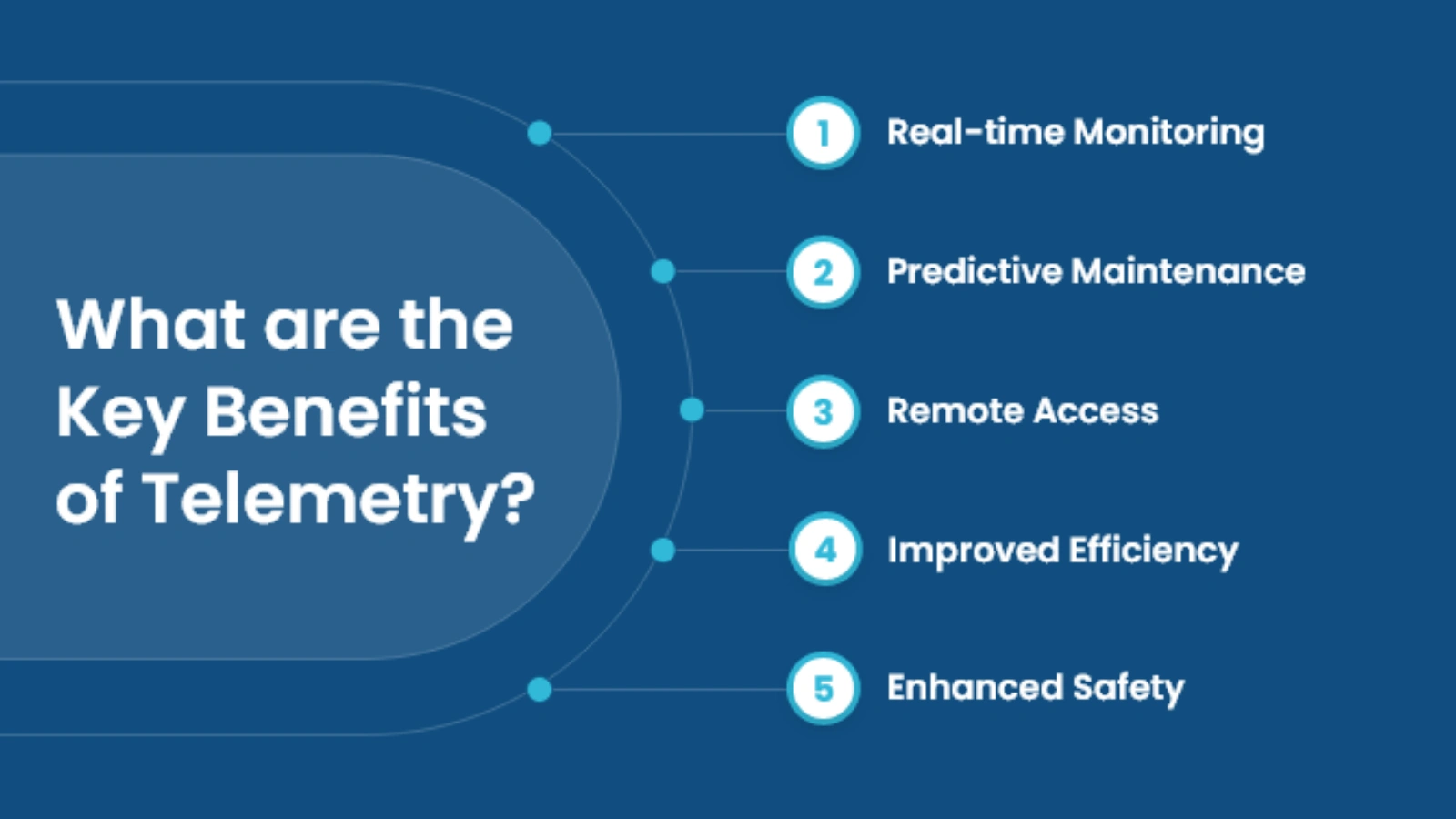
What Are Key Benefits Of Telemetry Data?
Businesses turn to telemetry data because it provides actionable insights and operational advantages. Some of the biggest benefits include:
1. Real-Time Monitoring:
Telemetry provides immediate visibility into processes, systems, and equipment. This allows organizations to detect irregularities quickly, prevent minor issues from escalating, and maintain consistent performance.
2. Predictive Insights:
By analyzing historical and current telemetry data, businesses can anticipate problems, forecast trends, and optimize resource allocation. This helps in proactive decision-making and preventive maintenance.
3. Enhanced Security:
Telemetry tracks activity across networks and systems, enabling early detection of suspicious behavior. Alerts generated from real-time data help organizations mitigate potential risks before they escalate.
4. Better Customer Experience:
Monitoring user behavior and usage patterns allows businesses to identify pain points, refine services, and personalize experiences. This leads to improved customer satisfaction and engagement.
5. Operational Efficiency:
Automating the collection and analysis of telemetry data reduces human error, saves time, and streamlines workflows. Teams can focus on strategic tasks instead of manual monitoring, boosting overall productivity.
How Is Telemetry Data Revolutionizing Different Industries?
The versatility of telemetry data makes it valuable across diverse sectors. Let’s explore its applications:
Healthcare:
Telemetry tracks patient vitals such as heart rate, oxygen levels, and blood pressure in real time. This helps doctors diagnose quickly and respond to emergencies with better accuracy.
Automotive:
Modern cars use telemetry to send diagnostics on fuel efficiency, tire pressure, and engine health. It also powers autonomous driving systems by providing continuous performance insights.
Aerospace:
Space agencies rely on telemetry to monitor spacecraft performance from millions of miles away. It ensures smooth mission control by detecting anomalies before they become risks.
IT & Business Operations:
Servers, apps, and networks generate telemetry to monitor uptime, optimize system performance, and detect threats. This prevents downtime and improves overall operational efficiency.
Workforce Monitoring:
Modern organizations use telemetry data within employee monitoring software to understand productivity, identify workflow bottlenecks, and maintain compliance in hybrid teams.
A practical example is EmpMonitor, an advanced employee monitoring and productivity management solution. By collecting real-time activity insights, it works much like telemetry systems, helping organizations track team efficiency, monitor workflows, and prevent security risks.
How Can EmpMonitor Use Telemetry Data To Boost Workforce Productivity?
When it comes to applying telemetry data in workforce environments, EmpMonitor stands out as a powerful solution. It blends telemetry-like monitoring with advanced analytics to give organizations a clear picture of how employees work, collaborate, and contribute.
Here’s how EmpMonitor leverages telemetry to enhance productivity:
Employee Monitoring Software:
EmpMonitor tracks the activity of distributed teams in real-time, giving managers visibility similar to telemetry dashboards. Context-rich reporting highlights team productivity trends, helping leaders identify areas for improvement and optimize workflows.
Time-Tracking:
Detailed timesheets capture active versus idle hours, revealing patterns in work habits and peak performance periods. This telemetry-like insight allows managers to accurately assess employee contributions and ensure accountability across projects.
User Activity Monitoring:
By continuously tracking applications, websites, and software usage, EmpMonitor provides a steady stream of data for decision-making. Managers can use these insights to streamline processes, prevent workflow bottlenecks, and ensure employees stay focused on high-priority tasks.
Insider Threat Prevention:
Just as telemetry systems flag anomalies in technical environments, EmpMonitor detects suspicious or potentially harmful activities. Early alerts help organizations mitigate risks from negligent or malicious actions, strengthening overall security for sensitive operations.
Attendance Monitoring:
EmpMonitor automates attendance and leave tracking, reducing administrative overhead and ensuring accuracy. Managers can access a centralized dashboard to monitor workforce presence, enforce compliance, and integrate attendance data with payroll seamlessly.
Real-Time Activity Tracking & Project Management:
Combining telemetry-style live tracking with project management, EmpMonitor monitors ongoing tasks, application use, and team progress. This provides leaders with actionable insights to allocate resources efficiently, identify delays, and foster effective collaboration across projects.
By leveraging EmpMonitor, organizations can transform telemetry data into actionable insights, driving higher productivity, better collaboration, and a more efficient workforce.
How Does Telemetry Data Drive Digital Transformation?
The push toward digital transformation has made telemetry data a necessity rather than an option. Companies are leveraging it to:
- Implement data-driven cultures where decisions are backed by real evidence.
- Adopt AI and machine learning to enhance predictive modeling.
- Improve customer personalization by tracking real-time behavior.
- Support compliance reporting with transparent, traceable insights.
Without telemetry, businesses risk falling behind in today’s competitive landscape.
What Are The Key Challenges Of Using Telemetry Data?
While telemetry data offers immense benefits, organizations often face several challenges when implementing and managing it:
1. Data Overload:
The volume of telemetry data generated can be massive, and without proper storage, filtering, and analytics tools, businesses may struggle to extract meaningful insights. Effective data management strategies are essential to avoid being overwhelmed.
2. Security Risks:
Continuous transmission of sensitive information can create vulnerabilities. Without robust encryption, secure networks, and access controls, telemetry data may be exposed to cyberattacks or unauthorized access.
3. Integration Issues:
Combining telemetry systems with existing legacy software or diverse IT infrastructures can be complex. Ensuring seamless interoperability requires careful planning, standardized protocols, and sometimes custom integration solutions.
4. Cost of Implementation:
High-quality telemetry systems, covering sensors, networks, cloud storage, and analytics tools, can demand significant upfront investment. Businesses must balance costs with expected efficiency gains and long-term ROI.
Addressing these challenges effectively requires a combination of the right technology, security measures, and strategic planning to fully leverage telemetry data’s potential.
Key Takeaways
- Telemetry data is information collected and transmitted from remote sources for monitoring and analysis.
- It powers industries ranging from healthcare to IT and plays a key role in employee productivity tools.
- Common telemetry data examples include fitness trackers, cars, and IT system monitoring.
- There are several telemetry types, such as wired, wireless, and IoT.
- Businesses must address challenges like data overload and security risks while implementing best practices.
- The future of telemetry will be shaped by AI, IoT, edge computing, and privacy concerns.
Final Thoughts
In a world defined by speed, innovation, and data-driven decisions, telemetry data is more relevant than ever. Its ability to provide real-time insights, predict outcomes, and drive efficiency makes it an indispensable tool for modern businesses and industries.
By investing in the right infrastructure and embracing best practices, companies can harness telemetry not just as a data source but as a powerful engine for growth, resilience, and innovation. Solutions like EmpMonitor take this a step further by turning workforce telemetry into actionable insights, helping organizations boost productivity, streamline operations, and enhance team performance.
FAQs
- What is telemetry data and why is it important?
Ans. Telemetry data is information collected remotely from devices or systems for real-time monitoring. It’s crucial for predictive insights, efficiency, and informed decision-making across industries. - What are the common types of telemetry data?
Ans. Telemetry data can be wired, wireless, satellite-based, or IoT-enabled, depending on the environment and application, allowing continuous monitoring at scale. - How is telemetry data used in different industries?
Ans. Industries like healthcare, automotive, aerospace, IT, and business operations use telemetry data to track performance, optimize processes, ensure safety, and improve productivity.