Quality assurance teams face a constant challenge: how do you maintain consistent standards across diverse processes while documenting issues effectively? The answer lies in screen recording, a powerful tool that’s transforming how organizations approach quality control, compliance, and process improvement. Through Screen Casting, teams can visually capture exactly how tasks are performed, errors occur, and systems respond in real time.
By capturing real-time workflows and interactions, businesses can identify bottlenecks, train teams more effectively, and maintain audit-ready documentation that stands up to scrutiny. Organizations that leverage screen recording gain a competitive advantage in maintaining quality standards.
In a business environment, quality assurance extends far beyond manufacturing floors. Software development, customer service, data entry, financial transactions, and countless other digital processes require meticulous oversight. Traditional QA methods like manual observation and written reports often miss critical details or fail to capture the full context of quality issues. This is where visual documentation becomes invaluable.
Listen To The Podcast Now!
Why Quality Assurance Teams Need Screen Recording?
Quality assurance isn’t just about catching mistakes; it’s about understanding why they happen and preventing them from recurring. When QA professionals can review exact sequences of actions, they gain insights that written reports simply cannot provide. Visual evidence eliminates ambiguity. When a quality issue arises, teams can point to specific moments in a workflow rather than relying on secondhand descriptions. This precision accelerates problem resolution and ensures everyone understands exactly what went wrong and how to fix it.
Documentation becomes standardized when organizations implement systematic recording practices. Instead of different team members creating varied reports with inconsistent detail levels, recorded sessions provide uniform, comprehensive records that anyone can review. Screen recording establishes a single source of truth for quality assessments.
Training new QA team members becomes significantly more efficient. Rather than shadowing experienced staff for weeks, new hires can watch recorded sessions that demonstrate proper procedures, common pitfalls, and best practices. This approach scales far better than one-on-one mentoring while maintaining quality standards. Compliance requirements in regulated industries often mandate detailed process documentation. Recorded workflows create audit trails that satisfy regulatory bodies while protecting organizations from potential compliance violations.
Key Applications in Organizational Quality Assurance:
1. Software Testing and Bug Documentation:
Software QA teams benefit immensely from capturing test sessions. When testers encounter bugs, a recording shows developers exactly what happened, the precise sequence of clicks, the system state, and any error messages. This eliminates the frustrating back-and-forth of “I can’t reproduce your issue.”
Regression testing becomes more reliable when teams can compare new software versions against recorded baseline behaviors. QA professionals can identify subtle changes in system performance or user interface responses that might otherwise go unnoticed.
2. Customer Service Quality Monitoring:
Contact centers use recordings to evaluate agent performance against established standards. Supervisors can review how agents navigate CRM systems, whether they follow required verification procedures, and if they access appropriate resources during customer interactions. Screen recording provides an unbiased view of actual agent behavior versus self-reported practices.
This application of employee screen recording provides objective performance data rather than relying solely on call monitoring or subjective observations. Agents receive concrete feedback with visual examples of areas for improvement.
3. Process Compliance Verification:
Financial institutions, healthcare organizations, and other regulated entities must prove their teams follow mandatory procedures. Recorded workflows demonstrate compliance during audits and investigations.
When discrepancies arise, compliance officers can review relevant sessions to determine whether proper protocols were followed. This capability proves invaluable during regulatory examinations or internal compliance reviews.
4. Training and Knowledge Transfer:
Creating training materials traditionally required extensive documentation writing and screenshot compilation. With recorded sessions, trainers can quickly produce realistic tutorials that show exactly how processes should be executed. Screen recording transforms knowledge transfer from a time-consuming manual process into an efficient, scalable system.
Subject matter experts can record their workflows once, creating reusable training resources that benefit multiple cohorts of new employees. This approach preserves institutional knowledge even when experienced staff members leave the organization.
Essential Features for QA Screen Recording Solutions:
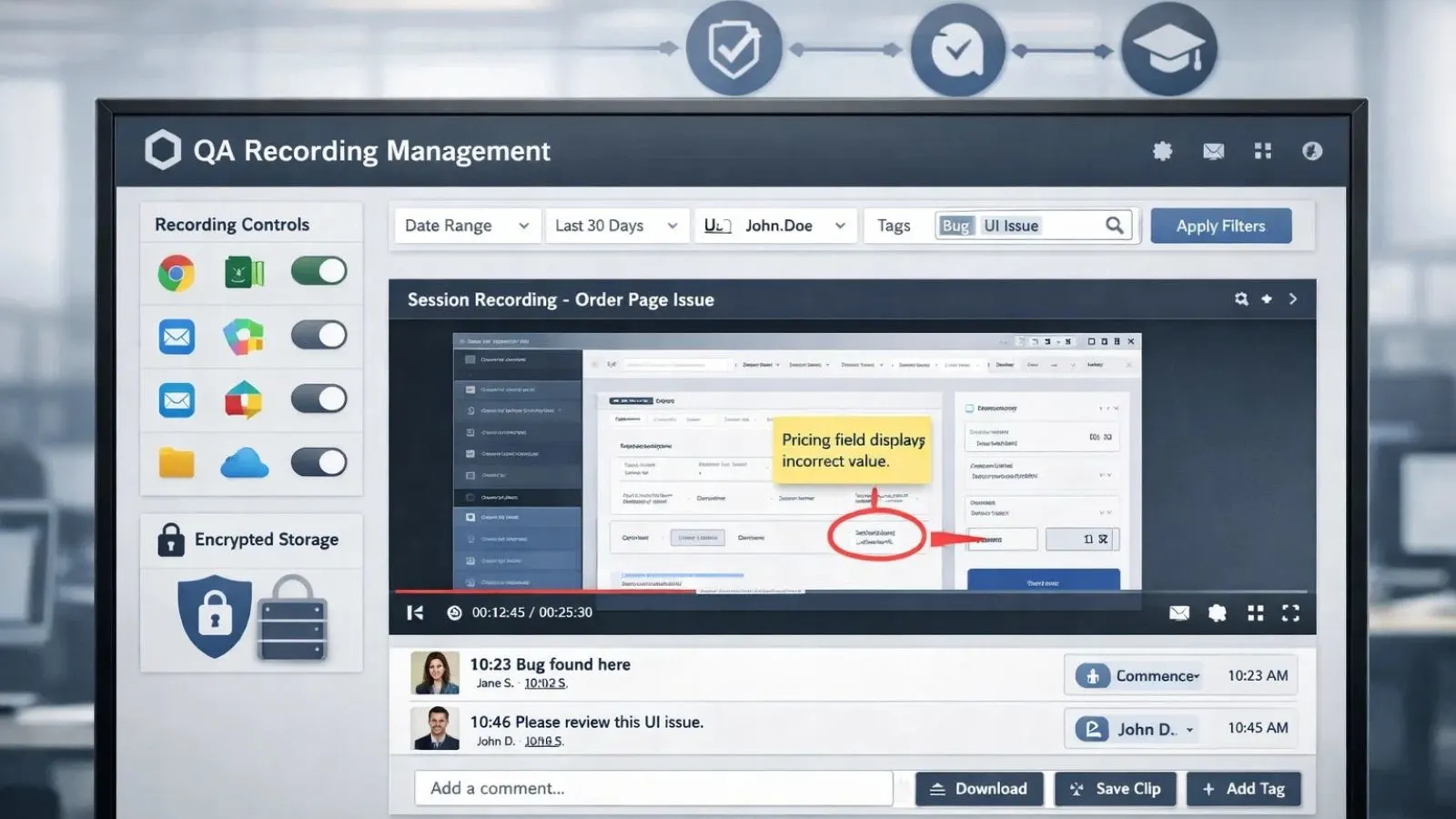
Not all recording tools meet quality assurance requirements. Organizations need solutions specifically designed for business environments with appropriate security, management, and analytical capabilities. When evaluating employee screen recording software, prioritize features that align with your quality objectives and compliance requirements.
1. Selective Recording Controls:
QA teams rarely need continuous recording of all activities. Effective solutions allow organizations to record specific applications, websites, or time periods relevant to quality monitoring. This targeted approach reduces storage requirements while focusing on priority processes.
2. Secure Storage and Access Management:
Quality assurance recordings often contain sensitive business information or personal data. Robust solutions provide encrypted storage, role-based access controls, and retention policies that align with data protection regulations.
3. Search and Retrieval Capabilities:
When managing thousands of recorded sessions, QA professionals need efficient ways to locate specific incidents. Advanced search functionality by date, user, application, or custom tags enables rapid retrieval of relevant recordings.
4. Annotation and Collaboration Tools:
QA reviewers should be able to add comments, timestamps, and annotations to recordings. These features facilitate team discussions and help document findings for corrective action tracking.
5. Integration with Existing Systems:
Standalone recording tools create silos. The best solutions integrate with ticketing systems, quality management platforms, and learning management systems to create seamless workflows.
Implementing Screen Recording in Your QA Program:
Successful implementation requires more than just purchasing software. Organizations must develop clear policies, train stakeholders, and establish governance structures.
1. Developing a Recording Policy:
Transparency is paramount. Employees should understand what gets recorded, why it’s necessary, and how the organization uses the data. Clear policies prevent misunderstandings and address privacy concerns upfront.
Define specific use cases for recordings in your policy. Specify which roles, departments, or processes fall under recording requirements. Clarity prevents scope creep and helps employees understand the program’s boundaries.
Establish retention schedules that balance regulatory requirements with storage limitations. Most organizations don’t need to keep routine recordings indefinitely; 30 to 90 days suffices for non-compliance-related quality monitoring.
2. Training QA Teams on Recording Analysis:
Reviewing recordings effectively requires skill development. QA analysts need training on identifying quality indicators, documenting findings consistently, and translating observations into actionable recommendations. Create standardized evaluation criteria and scoring rubrics.
This consistency ensures different reviewers assess recordings using the same quality standards, producing comparable results across the QA team. Develop escalation procedures for serious quality issues discovered during recording reviews. Clear protocols ensure critical problems receive immediate attention rather than getting lost in routine reporting. Screen recording becomes most valuable when it drives immediate corrective action.
3. Balancing Monitoring with Employee Trust:
Employee monitoring software implementations can create anxiety if not handled thoughtfully. Frame recording programs as quality improvement initiatives that benefit everyone, including employees who receive clearer feedback and recognition for excellence.
Avoid “gotcha” culture where recordings are primarily used for punitive purposes. When employees fear recordings will be weaponized against them, engagement and morale suffer. Instead, emphasize how recordings help identify training needs and process improvements.
Consider giving employees access to their own recordings. This transparency demonstrates trust and allows staff members to self-review their performance, fostering personal accountability and continuous improvement.
Also Read:
How EmpMonitor Enhances QA Screen Recording?
Organizations looking for serious quality assurance need more than basic screen recording; they need context, control, and clarity. EmpMonitor enhances QA by combining screen recording with live screen capture and workforce analytics, giving QA teams a complete, real-world view of how work actually happens.
Instead of isolated recordings, EmpMonitor delivers structured, searchable, and policy-driven visual evidence that supports audits, training, and continuous improvement, without unnecessary surveillance or data overload.
Key QA-Focused Features of EmpMonitor:
- Screen Recording & Live Screen Capture: Capture workflows in real time or review recorded sessions for detailed quality analysis.
- Selective Recording Rules: Record specific apps, users, or time windows to stay focused and compliant.
- Centralized QA Dashboard: Instantly search, filter, and review sessions from a single interface.
- Productivity & App Usage Context: Understand why quality issues occur, not just where.
- Insightful QA Reports: Spot trends, recurring errors, and top performers with actionable analytics.
The platform’s reporting features transform recorded data into actionable insights. Automated reports highlight quality trends, identify top performers, and flag recurring issues that warrant process redesign. This analytical layer turns raw recordings into strategic quality intelligence.
Overcoming Common Implementation Challenges:
Even well-planned recording programs encounter obstacles. Anticipating these challenges helps organizations develop mitigation strategies before problems escalate.
1. Technical Performance Issues:
Recording can impact system performance if not properly configured. Organizations should conduct pilot testing to identify resource requirements and optimize settings before full deployment. Modern solutions use efficient compression and selective recording to minimize performance impact.
Network bandwidth becomes a consideration when recordings are stored centrally or transmitted to cloud repositories. Evaluate infrastructure capacity and consider local caching or storage options if bandwidth limitations exist.
2. Employee Resistance:
Change management principles apply to recording program implementations. Communicate early and often about program objectives, address privacy concerns transparently, and involve employee representatives in policy development.
Highlight the benefits employees will experience, such as objective performance assessments, better training resources, and a reduced blame culture when issues arise. Making the “what’s in it for me” clear increases acceptance.
3. Data Overload:
Organizations can quickly accumulate massive recording libraries that become unmanageable. Implement automated retention policies that delete routine recordings after defined periods. Focus long-term storage on exceptional cases, training examples, and compliance-required documentation. Without proper data management, screen recording programs become unwieldy and lose effectiveness.
Use metadata tagging and categorization from the start. Consistent labeling makes future retrieval practical when recording volumes grow substantially.
Measuring QA Program Effectiveness:
Implementing recording capabilities is just the beginning. Organizations must assess whether these tools actually improve quality outcomes. Track key performance indicators like defect rates, compliance violations, customer complaints, and rework requirements. Effective recording programs should drive measurable improvements in these metrics over time.
Monitor training efficiency by comparing onboarding timelines and new employee performance before and after implementing recorded training materials. Reduced time-to-competency demonstrates program value. Survey both QA teams and monitored employees about program effectiveness. Gather feedback on whether recordings provide useful insights, if review processes feel fair, and where improvements would add value.
Calculate return on investment by comparing program costs against savings from reduced errors, faster problem resolution, decreased training expenses, and avoided compliance penalties. Quantifying benefits helps justify continued investment and potential program expansion.
Best Practices for Long-Term Success:
Sustainable QA recording programs evolve continuously rather than remaining static after initial deployment. Review and update recording policies annually to reflect changing business needs, technology capabilities, and regulatory requirements. What worked during initial implementation may need adjustment as your organization grows.
Regularly audit how recordings are actually being used versus intended purposes. Drift can occur where recordings get used for unintended purposes or fall into disuse in some departments. Periodic audits keep programs aligned with original objectives. Invest in ongoing training for both QA analysts and monitored employees. As teams become more sophisticated in using recorded data, they’ll identify new applications and opportunities that weren’t apparent initially. Continuous education maximizes the return on your screen recording investment.
Celebrate successes and share case studies internally. When quality improvements result from recording insights, publicize these wins to maintain stakeholder support and demonstrate program value.
Future Trends in QA Screen Recording:
Technology continues advancing, bringing new capabilities to quality assurance recording. Artificial intelligence is beginning to analyze recordings automatically, flagging potential quality issues without human review. Machine learning algorithms can identify patterns across thousands of sessions that would be impossible for manual reviewers to detect.
The concept of employee screen capture is evolving beyond simple video recording to include contextual data like application states, clipboard content, and system performance metrics. This richer data provides deeper insights into quality issues.
Digital forensics techniques are being adapted for quality assurance, allowing investigators to reconstruct complex incident sequences from multiple data sources beyond just screen recordings. Real-time quality monitoring is emerging, where AI assistants analyze activities as they occur and provide immediate guidance to employees. This proactive approach prevents quality issues rather than just documenting them after the fact.
Conclusion:
Screen recording has become indispensable for modern quality assurance programs. By providing objective, detailed documentation of workflows and processes, recording capabilities enable organizations to maintain higher standards, train more effectively, and satisfy compliance requirements. Success requires thoughtful implementation that balances monitoring needs with employee privacy, invests in proper tooling like EmpMonitor, and focuses on continuous improvement rather than punitive oversight. Organizations that embrace recording as a strategic quality tool position themselves for sustainable excellence.
FAQ’s:
Q1: How long should QA recordings be retained?
Ans: Retention periods depend on your industry and use case. For routine quality monitoring, 30-90 days typically suffices. Compliance-related recordings may require longer retention; consult your legal team and regulatory requirements.
Q2: Can employees refuse to be recorded?
Ans: This depends on jurisdiction and employment agreements. Most organizations make recording a condition of employment for roles where quality monitoring is essential. Transparency and clear policies are crucial.
Q3: What’s the difference between screen recording and employee monitoring software?
Ans: Employee monitoring software typically includes multiple capabilities beyond recording, such as activity tracking, productivity analytics, and application usage monitoring. Recording is one component of comprehensive monitoring solutions.
Q4: How much storage do QA recordings require?
Ans: Storage needs vary based on recording quality, duration, and volume. Modern compression reduces requirements significantly,expect approximately 100-300 MB per hour of recording. Cloud storage solutions scale as needed.